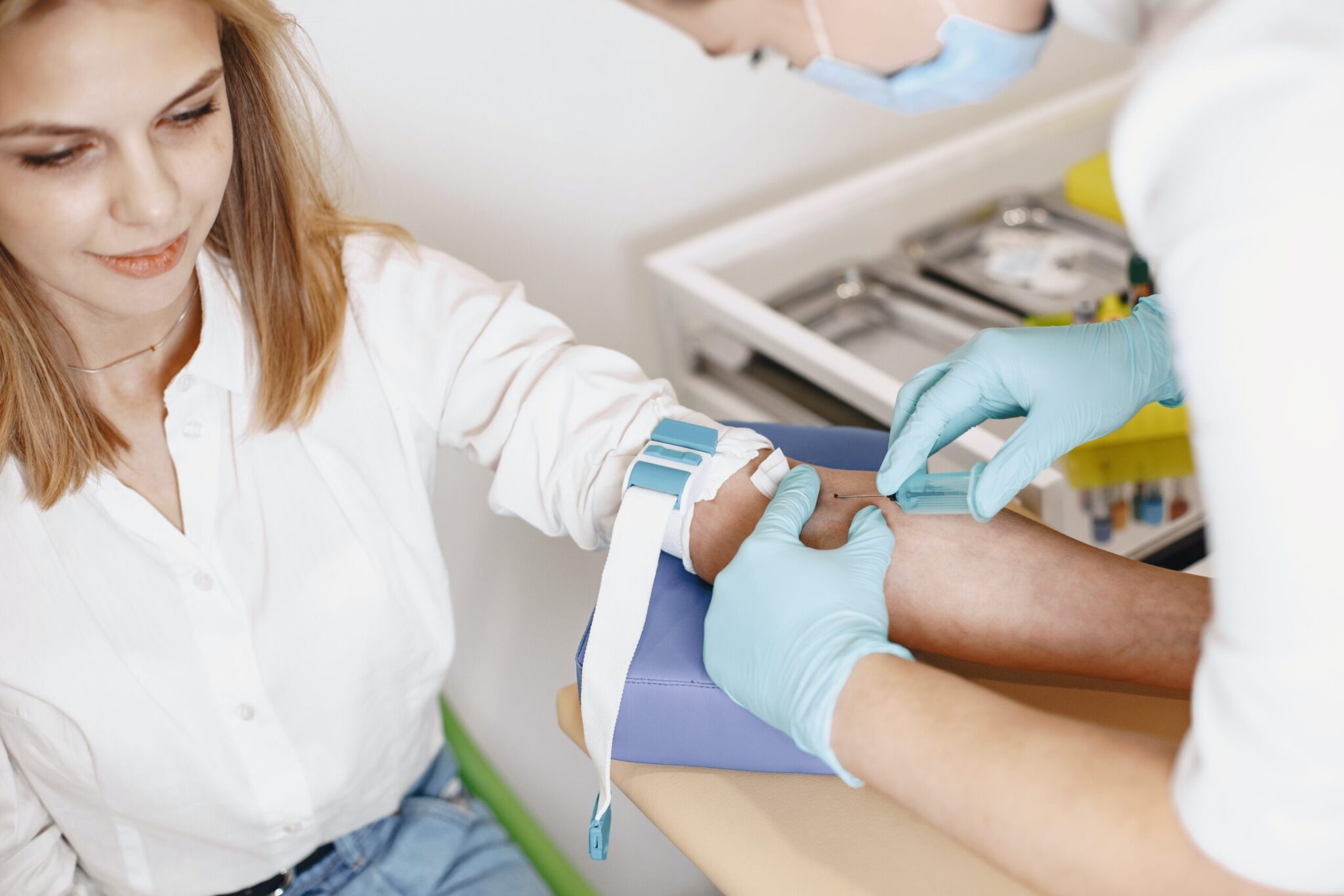
All healthcare providers are responsible for applying infection control measurements when caring for patients.
Infection prevention and control is paramount for several reasons, including patient safety, staff safety, disease prevention, public health, etc.
MANCOSA offers a short Infection Control for Healthcare course that teaches healthcare students the proper use of PPE, antiseptics, injection safety, and so much more.
In this article, we’ll discuss why disease control is essential and how healthcare workers prevent the spreading of infections and diseases. We’ll also uncover some of the fastest-growing trends and technologies that help decrease the spread of infections.
The reason why infection control is essential at healthcare facilities
Infection control, also called disease control, is vital in healthcare facilities, such as hospitals and clinics, since it prevents the patient and healthcare professional from disease.
Without it, hospitals would become a breeding ground for diseases and infections — making it unsafe for anyone to enter. This would result in widespread infectious diseases and viruses in the community and neighbouring cities.
The impact of infection control at healthcare facilities
Poor disease control can have a severe impact on healthcare facilities. It could lead to risks that impact patient safety.
- Inadequate hand hygiene: Hands are the main pathway of germs transmission during healthcare. This is because patients and healthcare professionals constantly touch things and move their hands to their mouths. Examples of diseases that can be transmitted by hand include influenza, chicken pox, the common cold, and meningitis.
- Improper use of PPE: Personal protective equipment, such as specialised clothing and equipment, should be worn by healthcare workers to protect themselves and patients against infectious materials. For example, a mask may be worn during patient treatment to prevent the transmission of bacteria.
- Inadequate cleaning and disinfection: Improper cleaning of equipment and surfaces can lead to cross-transmission of organisms. This means bacteria or microorganisms are unintentionally transferred from one object to another. This can cause cross infections, such as respiratory infections that spread to the eyes or ears.
- Lack of respiratory etiquette: Like hand hygiene, respiratory hygiene is part of the standard precautions healthcare facilities take to help prevent the spread of disease. Examples include covering your mouth when coughing, throwing the tissue away in a bin, etc.
- Improper use of medication safety standards: Healthcare professionals such as nurses and doctors must follow procedures for medication administration and safety standards. Failing to do so could spread infections and, in severe cases, even result in death. For example, they must throw away used needles. Otherwise, this could cause fatal blood infections.
The role of healthcare workers in infection control
Healthcare workers play a significant role in preventing infections in healthcare facilities. Generally, the infection prevention teams comprise a doctor and one or more nurses. Thus, good teamwork is often necessary in this environment. However, practitioners can sometimes work on their own.
Overall, healthcare workers are at the forefront of disease control efforts. Here are some of their most common duties regarding disease control:
- Adhere to standard procedures: They need to follow standard precautions to prevent the spreading of diseases and infections. These include proper use of PPE, such as gowns and masks, and adequate hand hygiene.
- Isolation precautions: Healthcare workers are responsible for identifying and implementing appropriate isolation requirements if they suspect contagious infections in a patient. This may include isolating the patient and adhering to specific contact precautions.
- Environmental cleaning: They must clean equipment and rooms to maintain a hygienic and safe environment. They do this by following the proper cleaning and disinfection protocols.
- Vaccination: Healthcare workers are encouraged to receive recommended vaccinations, such as hepatitis B, to protect themselves and patients from vaccine-preventable disease transmissions.
- Patient education: They educate patients and their families about infection prevention and protocols. This includes teaching patients about the appropriate use of PPE, respiratory etiquette, and other preventative measures to protect themselves and other patients.
Challenges faced in infection control
Infection prevention and control face several challenges that can impact its effectiveness. Here are some of these challenges:
- Lack of compliance: One of the biggest challenges is ensuring healthcare workers, patients, and visitors comply with the proper practices and measures.
- Limited resources: It requires a lot of resources, such as staff, equipment, supplies, and infrastructure, to prevent diseases from spreading. Thus, healthcare facilities often need to spend a lot of money on these resources, which is difficult with limited budgets.
- Poor communication: To prevent the spread of infections, good communication and teamwork between healthcare workers, patients, and families is paramount. Therefore, if communication is poor, people may accidentally fail to follow the proper protocols.
Emerging disease control strategies and technology
Here are some of the top strategies and technologies.
1. Artificial intelligence
Current infection management faces many challenges, such as the delay in detecting these infections, which can have a massive impact on quick response and prevention of spreading infections and diseases.
The healthcare industry has started to utilise artificial intelligence (AI) to detect these diseases faster and determine the most effective antibiotics for a specific infection.
2. Electronic health records (EHR)
EHR streamlines patient data management and enables healthcare workers to access critical patient information rapidly. This makes it much easier to control the spread of infections since doctors and nurses have real-time access to patient histories, laboratory results, and surveillance data.
3. Advanced sterilisation
Sterilised methods can be highly time-consuming and don’t eliminate all types of pathogens. This increases the risk of cross-contamination and infection spread.
Healthcare facilities have started to use sterilisation technologies, such as ultraviolet (UV) light, that offer rapid sterilisation of equipment and surfaces.
4. Telemedicine and telehealth
Telemedicine and telehealth enable healthcare workers to do remote consultations and monitor patients without being physically present. This reduces the need for in-person meetings, which can lead to disease transmission.
Explore the range of online MANCOSA health courses
If you’re ready to learn all you need to know about effective disease control, consider enrolling in our Infection Control course. This course only requires three days and will give you infection control training relevant to South African healthcare facilities.
You can also consider our other healthcare short courses to improve your skills, including the Good Clinical Practice short course and the Ethics for Healthcare Professionals course.


